
安妮 岳排槐 发自 凹非寺量子位 出品 | 公众号 QbitAI
如果你的心里只有一件事。
请问:是不是学习?
Google希望你是,而且还准备扶上马,再送一程。
所以今天一早,大礼包又来了。

手把手教你
今年春天,Google发布了机器学习速成课,英文简称MLCC。而且这套基本全程都有中文的课程,还是完全免费的。
这还不够。
Google觉得光学理论还不够,必须教你理论与实战相结合。
所谓:知行合一。
于是,Google发布了最新的一套课程:Machine Learning Practica(机器学习实践)。这套课程会示范Google如何在产品中使用机器学习。

课程地址在此:https://ift.tt/2kx5u5U
(.cn域名地址亲测可用)

与之前的课程不同,这套动手实践课程中,包括视频、文档和交互式编程练习。目前已经上线的第一课是图像分类。
在图像分类的实践课程中,可以学习Google如何开发利用最先进的图像分类模型,这也是Google相册背后的核心技术。
迄今为止,已有超过1万名Google员工利用这个实践课程来训练他们自己的图像分类器,最终实现可以识别照片中的猫猫狗狗。
课前准备
想要学习这套课程,也有一些基础要求。
主要是两点:
- 学过Google机器学习速成课,或者了解机器学习的基本概念
- 有不错的编程基础知识,以及有一些Python编程经验
这套实践课程使用了Keras API。以及课程中的编程练习,使用了Colab。使用Colab不要求之前有过Keras经验。
课程中代码基本可算是提供了逐步的解释。
目前这套实践课程只发布了图像分类一组,但Google表示更多的实践课程正在:肮!啧!味!

课程简介
在这个课程中,Google首先介绍了图像分类的基本原理,讲述了卷积神经网络(CNN)的构建,以及池化、全连接等概念。
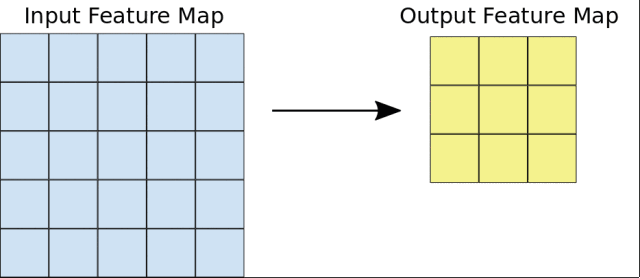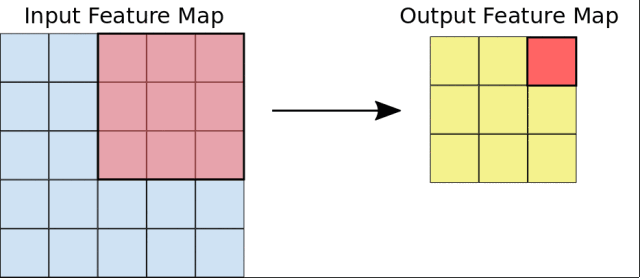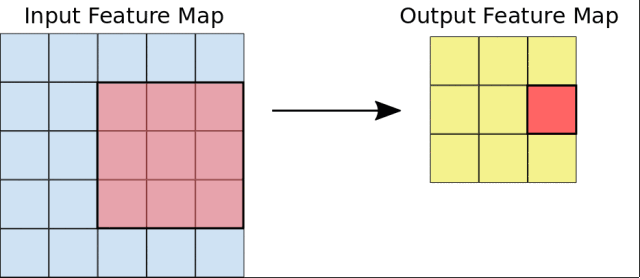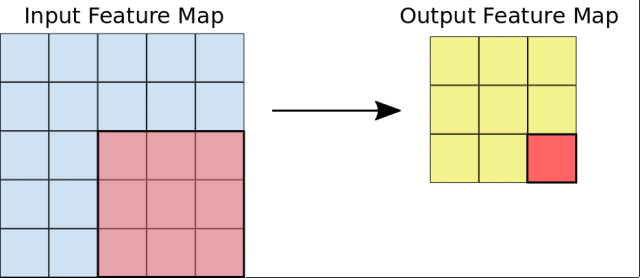
然后,Google会引导你从头开始构建一个CNN网络,并且学习如何防止过拟合,以及利用训练模型进行特征提取和微调。
实践课程一共包括三组练习,分别是:
- Exercise 1: Build a Convnet for Cat-vs-Dog Classification带你构建一个猫狗分类的卷积网络。
- Exercise 2: Preventing Overfitting教你如何防止过拟合,改善提高CNN模型。
- Exercise 3: Feature Extraction and Fine-Tuning教你如何通过特征提取和微调来使用Google的Inception v3模型,并为上面两个练习完成的分类器获取更好的准确性。
课程示范
量子位潜入这个课程内部,带回了第二个实践练习。在这堂课里,谷歌想教会大家在猫狗图像分类中,如何减少过拟合。大家感受一下——

练习2:减少过拟合
预计完成时间:30分钟
在本节练习中,我们将基于在练习1中创建的模型将猫狗分类,并通过一些策略减少过拟合:也就是数据增强(Data Augmentation)和正则化方法dropout,从而提高准确性。
和长颈鹿被关进冰箱一样,这得分四步走:
- 通过对训练图像进行随机转换,来探索数据增强的玩法
- 在我们数据处理的过程中应用数据增强
- 在转换中加入dropout
- 重新训练模型,评估损失和精确度
Let's get started吧!

数据增强の探索
数据增强是减少视觉模型过拟合的基本方法了,因为我们手头的训练实例为数不多,为了充分利用,我们可通过一些随机的变换"增强"它们,对模型来说,这是不同的图像~
这可以通过在ImageDataGenerator实例读取的图像上增加一些随机转换来实现,比如:
1 from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator 2 3 datagen = ImageDataGenerator( 4 rotation_range=40, 5 width_shift_range=0.2, 6 height_shift_range=0.2, 7 shear_range=0.2, 8 zoom_range=0.2, 9 horizontal_flip=True, 10 fill_mode='nearest')
还有一些可用的选择:
- rotation_range是在0-180之间的一个值,可在此角度内随机旋转图片。
- width_shift和height_shift是个范围,指的总宽度或高度的一部分,图像可在此范围内垂直或水平随机转换。
- shear_range用于随机剪切。
- zoom_range用来随机缩放图片的。
- horizontal_flip用于水平随机翻转图像的一半。
- fill_mode是用来填充新创造的像素,在图像随机垂直或水平变换后可能用到
注意:此练习中使用的2000张图片摘自Kaggle上的"狗vs猫"数据集,包含25000张图片。为了节约训练时间,这里我们只用到其中的一个子集。
1 !wget --no-check-certificate \ 2 https://storage.googleapis.com/mledu-datasets/cats_and_dogs_filtered.zip -O \ 3 /tmp/cats_and_dogs_filtered.zip
1 import os 2 import zipfile 3 4 local_zip = '/tmp/cats_and_dogs_filtered.zip' 5 zip_ref = zipfile.ZipFile(local_zip, 'r') 6 zip_ref.extractall('/tmp') 7 zip_ref.close() 8 9 base_dir = '/tmp/cats_and_dogs_filtered' 10 train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'train') 11 validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'validation') 12 13 # Directory with our training cat pictures 14 train_cats_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'cats') 15 16 # Directory with our training dog pictures 17 train_dogs_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'dogs') 18 19 # Directory with our validation cat pictures 20 validation_cats_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'cats') 21 22 # Directory with our validation dog pictures 23 validation_dogs_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'dogs') 24 25 train_cat_fnames = os.listdir(train_cats_dir) 26 train_dog_fnames = os.listdir(train_dogs_dir)
接下来,我们将datagen转换应用到训练集里的猫咪图像,生成5个随机变量。这个单元需多运行几次,找到新批次中的随机变量。
1 %matplotlib inline 2 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import matplotlib.image as mpimg 5 6 from keras.preprocessing.image import array_to_img, img_to_array, load_img 7 8 img_path = os.path.join(train_cats_dir, train_cat_fnames[2]) 9 img = load_img(img_path, target_size=(150, 150)) # this is a PIL image 10 x = img_to_array(img) # Numpy array with shape (150, 150, 3) 11 x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape) # Numpy array with shape (1, 150, 150, 3) 12 13 # The .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images 14 # It will loop indefinitely, so we need to `break` the loop at some point! 15 i = 0 16 for batch in datagen.flow(x, batch_size=1): 17 plt.figure(i) 18 imgplot = plt.imshow(array_to_img(batch[0])) 19 i += 1 20 if i % 5 == 0: 21 break
在数据处理过程中应用数据增强
现在,将上述增强的数据应用到数据预处理配置中——
1 # Adding rescale, rotation_range, width_shift_range, height_shift_range, 2 # shear_range, zoom_range, and horizontal flip to our ImageDataGenerator 3 train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator( 4 rescale=1./255, 5 rotation_range=40, 6 width_shift_range=0.2, 7 height_shift_range=0.2, 8 shear_range=0.2, 9 zoom_range=0.2, 10 horizontal_flip=True,) 11 12 # Note that the validation data should not be augmented! 13 test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255) 14 15 # Flow training images in batches of 32 using train_datagen generator 16 train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory( 17 train_dir, # This is the source directory for training images 18 target_size=(150, 150), # All images will be resized to 150x150 19 batch_size=20, 20 # Since we use binary_crossentropy loss, we need binary labels 21 class_mode='binary') 22 23 # Flow validation images in batches of 32 using test_datagen generator 24 validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory( 25 validation_dir, 26 target_size=(150, 150), 27 batch_size=20, 28 class_mode='binary')
神奇之处是,若用增强的数据来训练模型,则不会被认为是相同示例(虽然它们都是从一张图片上得到的)。不过模型眼中这些输入仍紧密相关的,所以还不足以完全消除过拟合。
加入Dropout
不过~还有另外一种流行的策略能减少过拟合,即dropout。
如果你想了解过拟合的基本概念,这里自卖自夸推荐两个之前免费课程中的相关介绍:
https://ift.tt/2sprPpN
https://ift.tt/2taZsiT
我们从练习1重新配置我们的convnet架构,在最后的分类层前试图添加一些dropout。
1 from keras.models import Model 2 from keras import layers 3 from keras.optimizers import RMSprop 4 from keras import backend as K 5 6 import tensorflow as tf 7 8 # Configure the TF backend session 9 tf_config = tf.ConfigProto( 10 gpu_options=tf.GPUOptions(allow_growth=True)) 11 K.set_session(tf.Session(config=tf_config)) 12 13 # Our input feature map is 150x150x3: 150x150 for the image pixels, and 3 for 14 # the three color channels: R, G, and B 15 img_input = layers.Input(shape=(150, 150, 3)) 16 17 # First convolution extracts 16 filters that are 3x3 18 # Convolution is followed by max-pooling layer with a 2x2 window 19 x = layers.Conv2D(16, 3, activation='relu')(img_input) 20 x = layers.MaxPooling2D(2)(x) 21 22 # Second convolution extracts 32 filters that are 3x3 23 # Convolution is followed by max-pooling layer with a 2x2 window 24 x = layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu')(x) 25 x = layers.MaxPooling2D(2)(x) 26 27 # Third convolution extracts 64 filters that are 3x3 28 # Convolution is followed by max-pooling layer with a 2x2 window 29 x = layers.Convolution2D(64, 3, activation='relu')(x) 30 x = layers.MaxPooling2D(2)(x) 31 32 # Flatten feature map to a 1-dim tensor 33 x = layers.Flatten()(x) 34 35 # Create a fully connected layer with ReLU activation and 512 hidden units 36 x = layers.Dense(512, activation='relu')(x) 37 38 # Add a dropout rate of 0.5 39 x = layers.Dropout(0.5)(x) 40 41 # Create output layer with a single node and sigmoid activation 42 output = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(x) 43 44 # Configure and compile the model 45 model = Model(img_input, output) 46 model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', 47 optimizer=RMSprop(lr=0.001), 48 metrics=['acc'])
重新训练模型
随着数据的增加和dropout的填入,我们需要重新训练convnet模型。
这一次,我们训练全部的2000张图片,训练了30轮,并对验证了所有的1000个测试图像。
这可能需要几分钟的时间,检验一下你是否能自己编写代码了。
1 # WRITE CODE TO TRAIN THE MODEL ON ALL 2000 IMAGES FOR 30 EPOCHS, AND VALIDATE 2 # ON ALL 1,000 TEST IMAGES评估结果
接下来,我们用数据增强和dropout评估模型训练的结果。
1 # Retrieve a list of accuracy results on training and test data 2 # sets for each training epoch 3 acc = history.history['acc'] 4 val_acc = history.history['val_acc'] 5 6 # Retrieve a list of list results on training and test data 7 # sets for each training epoch 8 loss = history.history['loss'] 9 val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] 10 11 # Get number of epochs 12 epochs = range(len(acc)) 13 14 # Plot training and validation accuracy per epoch 15 plt.plot(epochs, acc) 16 plt.plot(epochs, val_acc) 17 plt.title('Training and validation accuracy') 18 19 plt.figure() 20 21 # Plot training and validation loss per epoch 22 plt.plot(epochs, loss) 23 plt.plot(epochs, val_loss) 24 plt.title('Training and validation loss')
结果不错!模型已经不再过拟合。
事实上,从我们的训练资料来看,随着训练次数的增加,模型的准确度会达到80%!
清理
在运行练习3之前,我们还需要运行以下单元来释放kernel和空闲的内存资源:
1 import os, signal 2 os.kill(os.getpid(), signal.SIGKILL)One More Thing
不知道是不是忙中出错,Google这套全新的课程,在我们发稿的时候,遇到了一个尴尬的问题:练习课程无法访问。
你点击练习之后,原本应该是转入一个Colab页面,但是却把多数用户挡在一个这样的界面之上。如图:
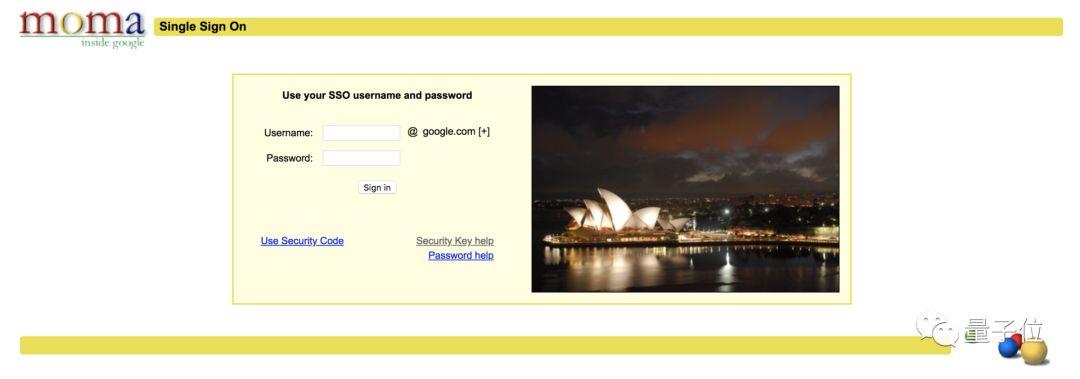
链接地址:https://ift.tt/19rEps4
这是啥?
其实,这就是大名鼎鼎的moma,一个Google内部的搜索工具。如果你是Google员工,就能登录访问,进入Google内网。
可能是因为这套实践课程,和MLCC一样,也是之前面向Google内部的课程,所以出现了现在略微尴尬的一幕。
估计,可能很快会修复这个问题。
所以你可以先看看上面量子位搬运的课程示范。
不急。
可以先看看之前可用的课程。

— 完 —
欢迎大家关注我们的专栏:量子位 - 知乎专栏
诚挚招聘量子位正在招募编辑/记者,工作地点在北京中关村。期待有才气、有热情的同学加入我们!相关细节,请在量子位公众号(QbitAI)对话界面,回复"招聘"两个字。量子位 QbitAI · 头条号签约作者վ'ᴗ' ի 追踪AI技术和产品新动态


没有评论:
发表评论